Introduction to History
History
History is a fascinating subject that provides a window into the past, allowing us to understand the events, cultures, and people that have shaped our world. From ancient civilizations to modern times, history covers a vast array of topics and periods. This article explores the significance of history, notable historical periods, and the importance of preserving our historical heritage.

The Importance of Studying History
Studying history is essential for several reasons:
- Understanding Human Progress: History shows how societies have evolved over time, highlighting achievements, struggles, and milestones.
- Learning from the Past: By examining past mistakes and successes, we can make informed decisions for the future.
- Cultural Appreciation: History provides insight into different cultures, fostering empathy and global awareness.
- Identity and Continuity: Understanding our past helps us appreciate our heritage and identity.

Notable Historical Periods
- Ancient Civilizations:
– Mesopotamia: Often considered the cradle of civilization, Mesopotamia introduced writing, law, and urbanization.
– Ancient Egypt: Known for its pyramids, pharaohs, and contributions to mathematics and medicine.
Indus Valley: An advanced civilization with well-planned cities and a unique script.

2. Classical Antiquity
– Ancient Greece: Birthplace of democracy, philosophy, and the Olympic Games.
– Ancient Rome: Renowned for its engineering, law, and the expansion of the Roman Empire.
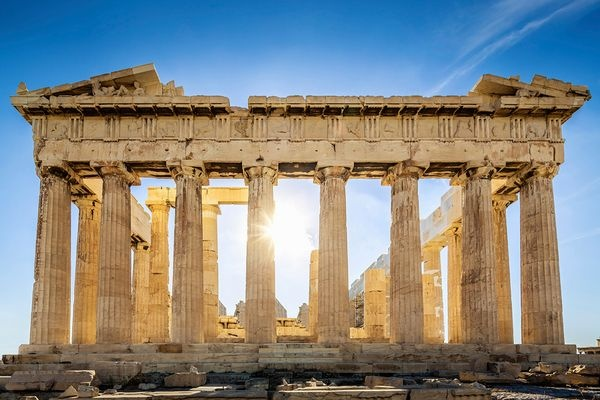

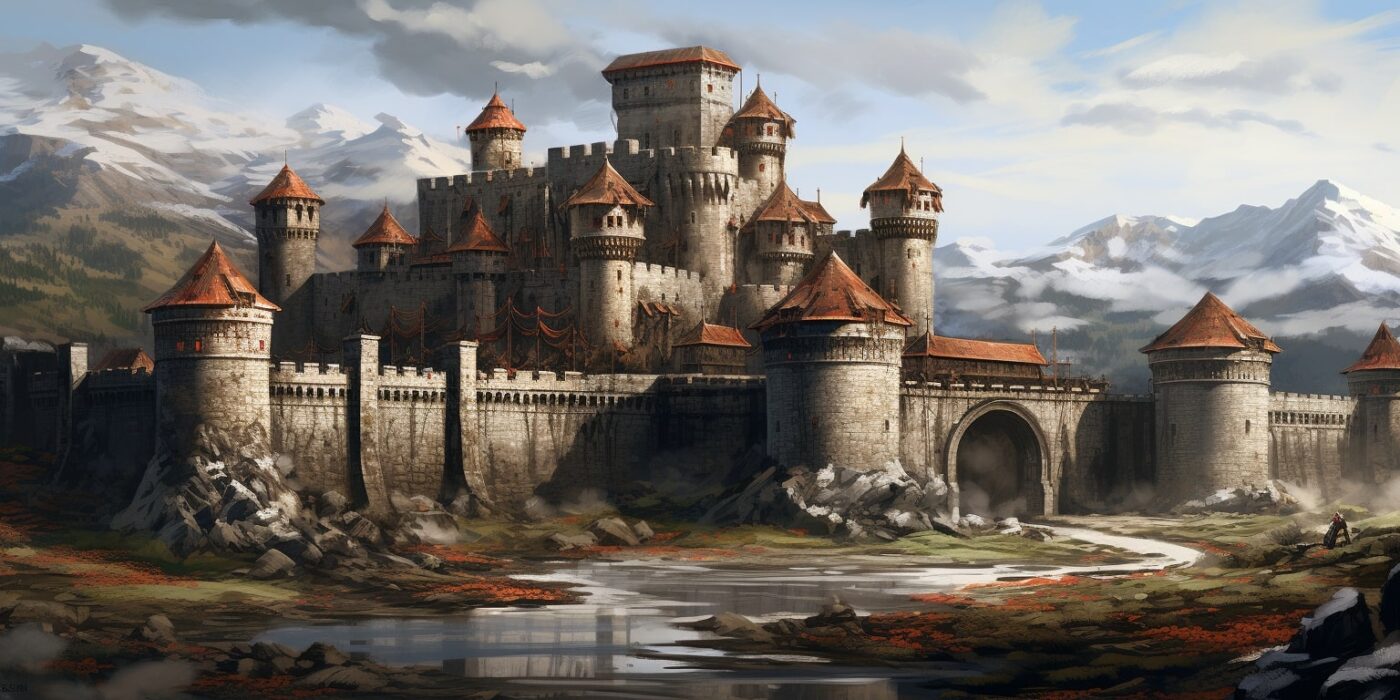
3. Middle Ages
– Feudal Europe: Characterized by castles, knights, and the rise of monarchies.
– Islamic Golden Age: A period of significant advancements in science, medicine, and culture in the ‘ Islamic world.

4. Renaissance and Enlightenment
– Renaissance: A cultural rebirth in Europe, emphasizing art, literature, and science.
– Enlightenment: An intellectual movement advocating reason, individualism, and scientific progress.
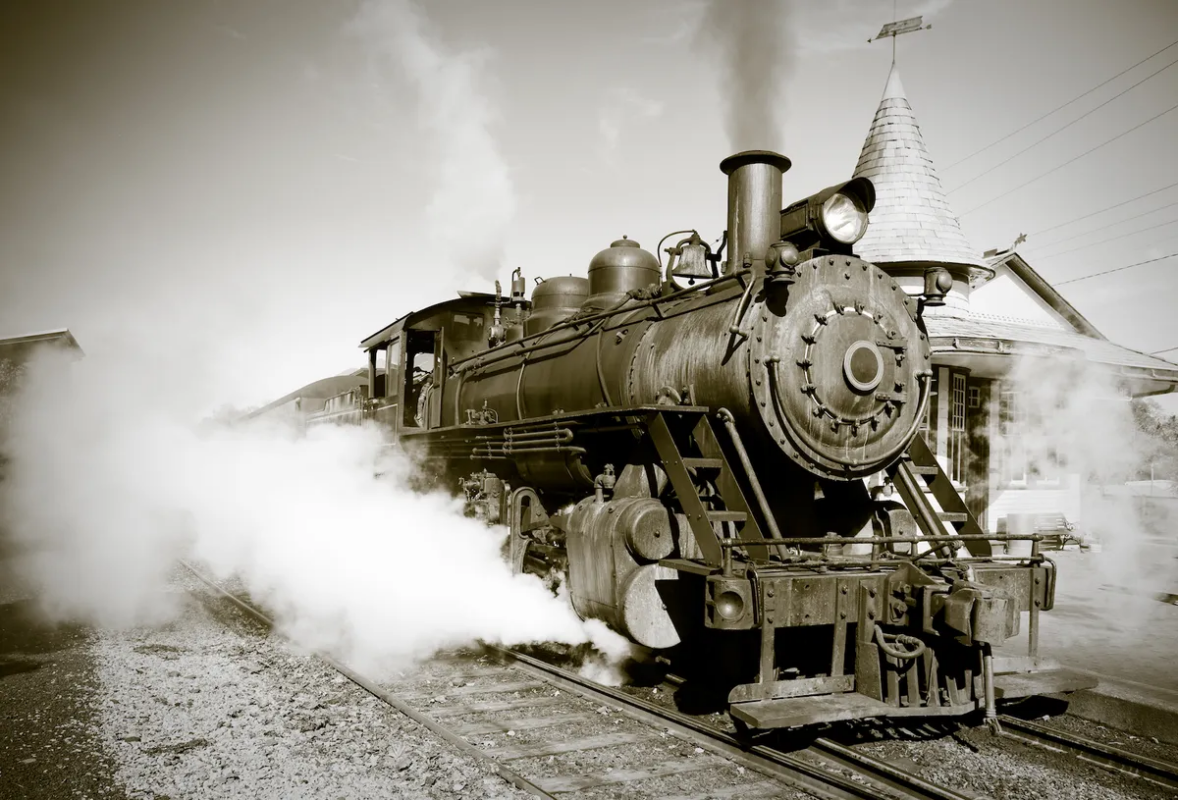
5. Modern Era
– Industrial Revolution: A period of technological advancements and industrial growth.
– World Wars: Significant global conflicts that shaped the 20th century.
– Digital Age: The rapid advancement of technology and the internet revolutionizing communication ‘ and information.

Preserving Historical Heritage
Preserving our historical heritage is crucial for future generations. Efforts include:
- Museums and Archives: Institutions that protect and display historical artifacts.
- Historic Sites: Preserved locations that offer a glimpse into the past.
- Education and Research: Encouraging the study and documentation of history through academic institutions and research.
Conclusion
- History is a vital subject that connects us to our past and informs our future. By studying history, we gain a deeper understanding of human civilization and the diverse cultures that populate our world. Preserving historical knowledge and heritage ensures that future generations can learn from and appreciate the rich tapestry of human experience.