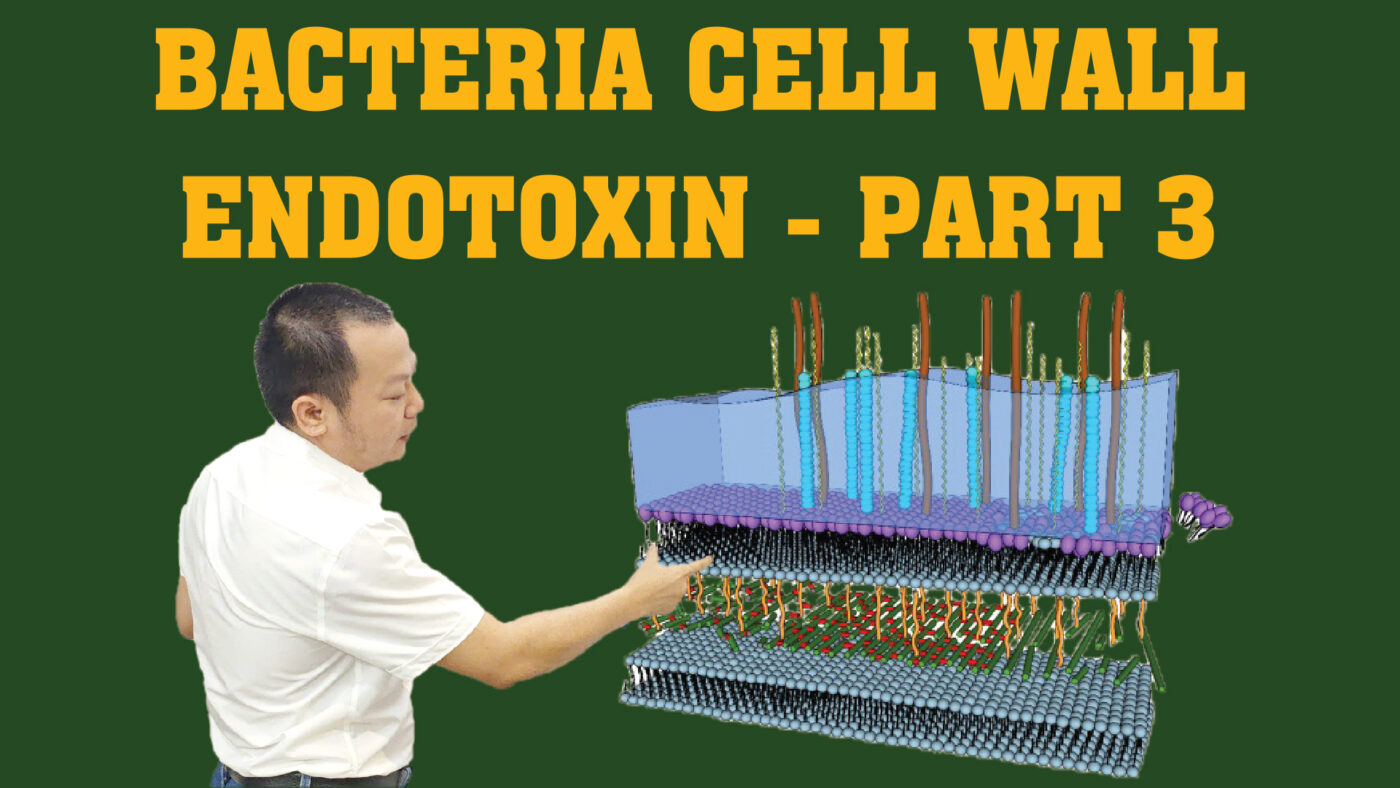
Bacteria Cell Wall Endotoxin
I. Introduction to Bacteria Cell Wall Endotoxin
The term endotoxin refers to components of the bacterial cell wall, particularly found in Gram-negative bacteria. These endotoxins, primarily lipopolysaccharides (LPS), play a critical role in bacterial survival and pathogenicity. In Part 3 of our exploration, we delve deeper into the biological mechanisms, immune responses, and the clinical significance of endotoxins.
Understanding the nuances of bacteria cell wall endotoxins is essential for medical research and therapeutic advancements. Their profound impact on human health makes them a central focus in microbiology and immunology.
II. Structure of Bacteria Cell Wall Endotoxins
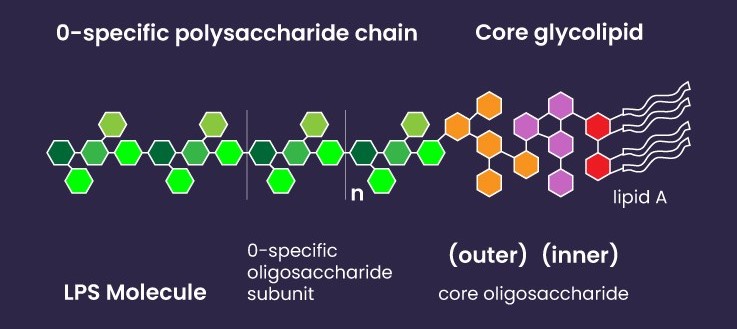
1. Composition of Lipopolysaccharides (LPS)
The bacterial cell wall endotoxin is composed of three main parts:
- Lipid A: Anchors the endotoxin to the outer membrane and is the primary toxic component.
- Core Polysaccharide: Connects Lipid A to the O-antigen.
- O-antigen: A variable region that determines the immunogenicity of the endotoxin.
This unique structure is responsible for the endotoxin’s robust resistance to environmental changes and its ability to trigger immune responses.
2. Role of Endotoxins in Bacterial Survival
Endotoxins contribute to bacterial resistance against antimicrobial agents and environmental stress. The Lipid A portion, in particular, provides protection against host immune defenses, ensuring bacterial persistence in hostile environments.
III. Mechanisms of Immune Response to Endotoxins
1. Detection by Host Immune System
The human immune system recognizes endotoxins through pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), such as Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). This recognition triggers a cascade of signaling events that lead to inflammation.
2. Cytokine Storm and Sepsis
One of the most dangerous outcomes of endotoxin exposure is a cytokine storm. This overreaction of the immune system can result in:
- Severe inflammation
- Organ damage
- Septic shock
3. Modulation of Immune Responses
Interestingly, low doses of endotoxins can sometimes prime the immune system, enhancing its ability to fight infections. This phenomenon, termed endotoxin tolerance, has potential therapeutic implications.
IV. Clinical Implications of Endotoxins
1. Endotoxins in Infections and Diseases
Endotoxins are implicated in numerous conditions, including:
- Sepsis: A life-threatening response to infection where endotoxins play a central role.
- Chronic Inflammation: Persistent exposure to endotoxins can exacerbate diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis.
2. Role in Diagnostic and Therapeutic Development
The detection of endotoxins in clinical settings is vital for:
- Diagnosing bacterial infections.
- Monitoring contamination in medical devices and pharmaceuticals.
3. Endotoxins in Vaccine Development
Endotoxins have been leveraged to develop vaccines, either as adjuvants to boost immunity or as antigens to trigger specific immune responses.
V. Endotoxin Removal and Neutralization Strategies
1. Medical Approaches to Endotoxin Detoxification
Techniques to mitigate endotoxin effects include:
- Polymyxins: Antibiotics that bind to Lipid A, neutralizing its toxic effects.
- Hemoperfusion: Filters endotoxins from the bloodstream during sepsis.
2. Biotechnological Applications
Recent advancements in biotechnology offer innovative approaches to reduce endotoxin contamination in drug production, such as endotoxin-specific resins and filtration systems.
VI. Research Frontiers in Bacteria Cell Wall Endotoxins
1. Genomic Insights
With advancements in genomics, researchers are unraveling the genetic pathways that regulate endotoxin production in bacteria. This knowledge can lead to novel antimicrobial strategies.
2. Synthetic Biology Applications
Synthetic biology is being utilized to engineer bacteria with modified endotoxins. These modifications aim to reduce virulence while maintaining immunogenicity, aiding in vaccine development.
3. Future Therapies
New therapeutics targeting endotoxin signaling pathways, such as TLR4 inhibitors, show promise in mitigating inflammation without compromising immunity.
VII. Conclusion
The study of bacteria cell wall endotoxins is an ever-evolving field that bridges microbiology, immunology, and clinical medicine. From their structural complexity to their profound impact on health, endotoxins are central to understanding bacterial pathogenesis.
Efforts to neutralize their harmful effects while harnessing their potential benefits hold great promise for future healthcare advancements. Continued research will undoubtedly unlock more secrets of these fascinating yet formidable molecules.
By exploring Bacteria Cell Wall Endotoxin – Part 3, we gain a comprehensive understanding of their mechanisms, clinical significance, and the innovative strategies being developed to manage their impact.
This article provides a detailed, SEO-optimized insight into bacteria cell wall endotoxins. For further updates, stay tuned for upcoming discussions on this critical topic!
Xem thêm video tại:
https://www.youtube.com/@learnabcacademy
Trang chủ LearnABC Education:
https://learnabcacademy.com/
Theo dõi thêm các bài viết tại:
https://huynhtrunutrition.com/
Hãy học cách phòng ngừa thay vì bệnh rồi mới tìm cách chữa trị. Tham khảo 2 tập của sách Ayurveda, link mua sách tại:
http://huynhtruayurveda.com

Câu hỏi thắc mắc, vui lòng liên hệ:
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LUYENPHATAM